Week7 Life in Silico & CRISPR
Assignments
Homework:
- Explain, draw/sketch and understand the CRISPR/Cas9 mechanism. Name the involved parts, expand and learn the acronym, explain why this technology is a break-through, explain how it can be programmed.
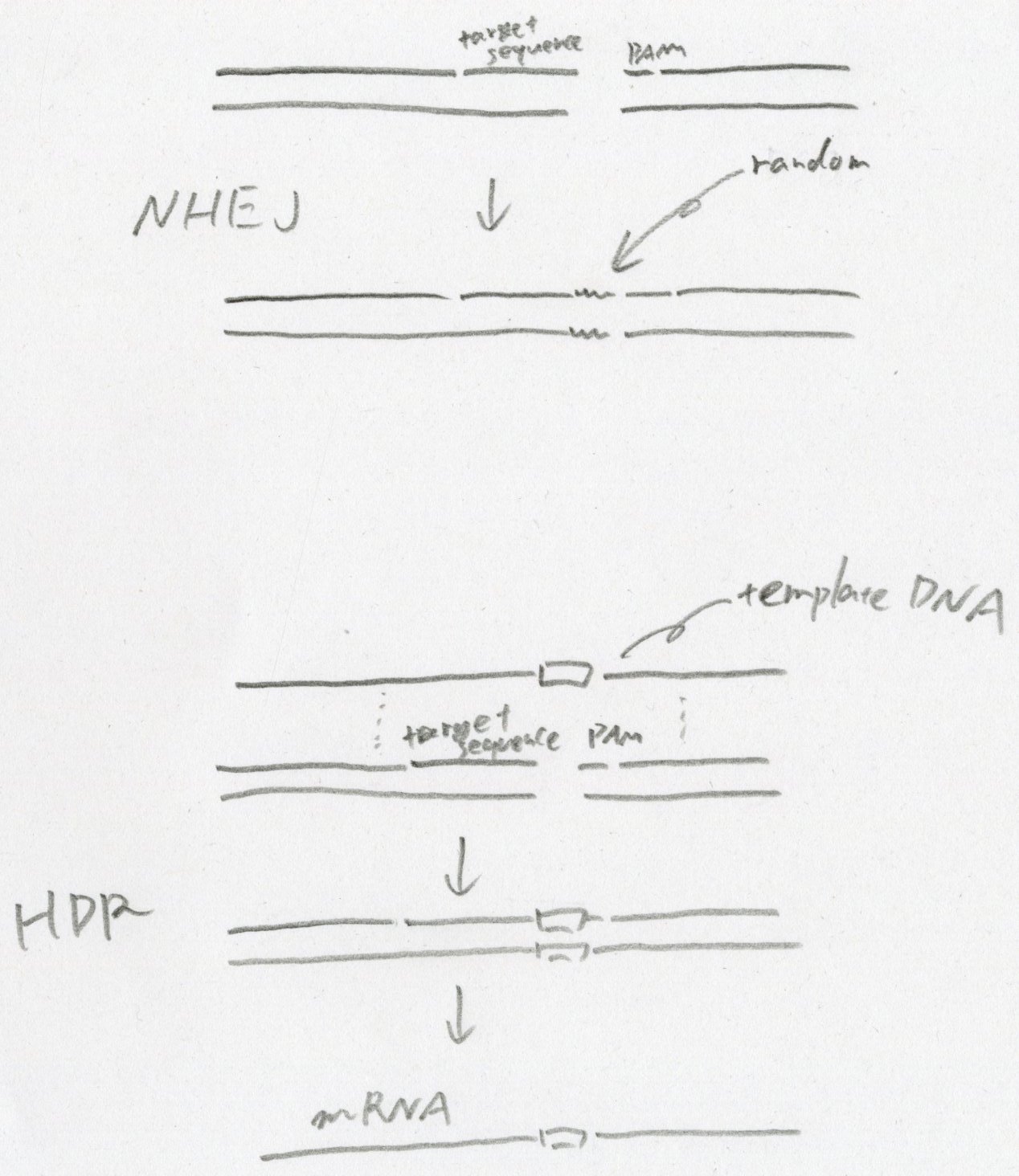
- Explain, draw/sketch and understand the DNA Repair mechanisms: HDR and NHEH
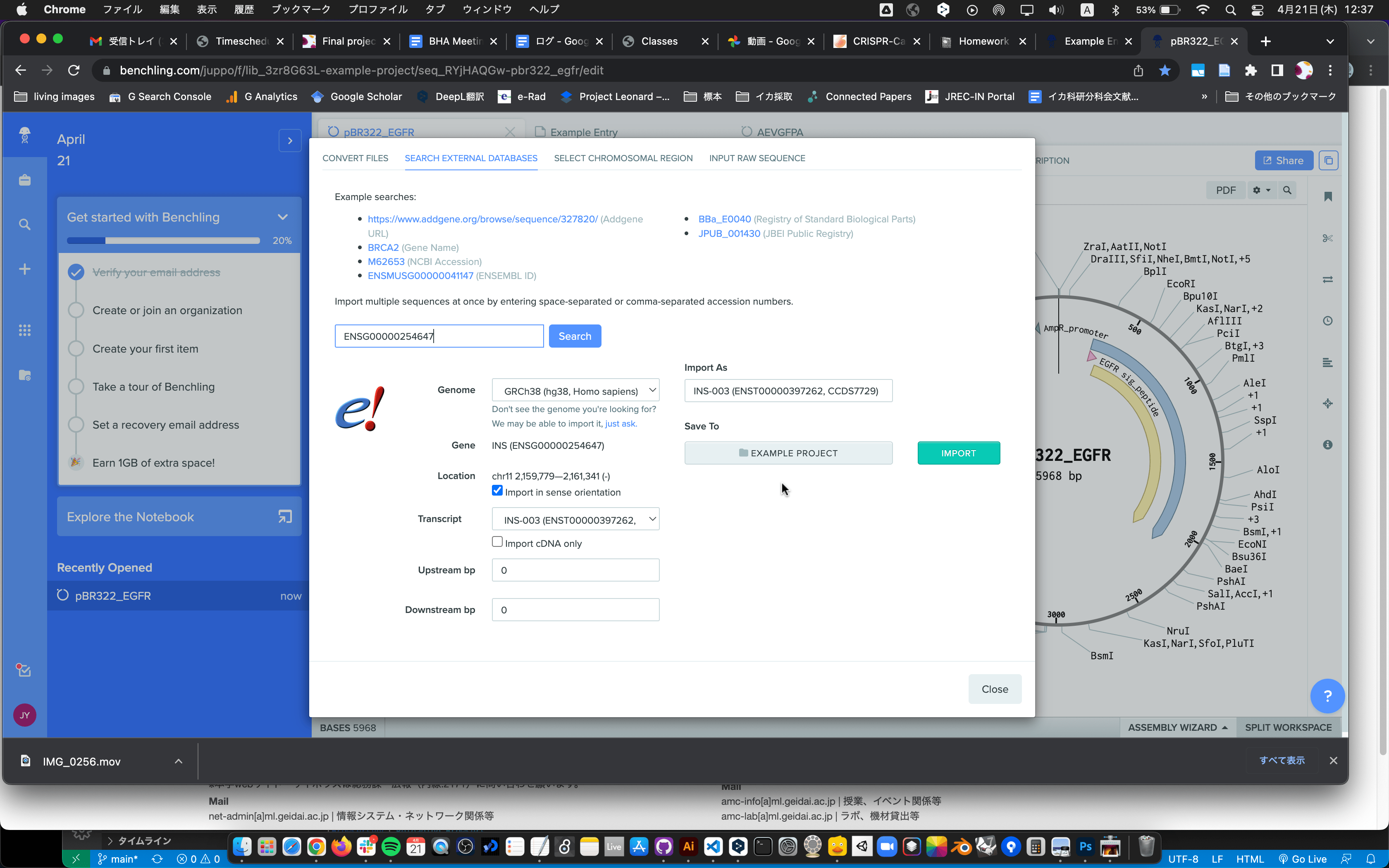
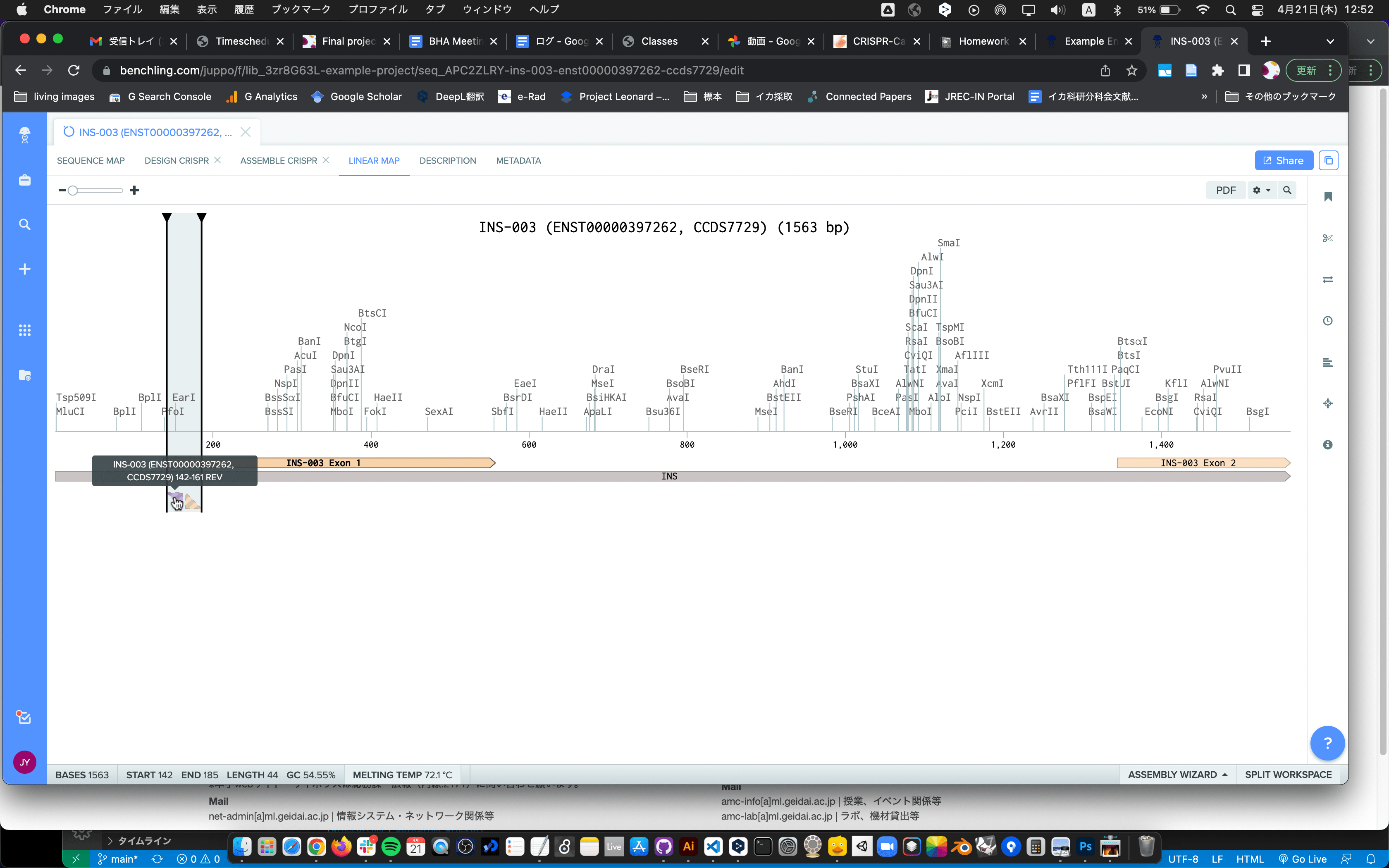
- Make an account at benchling.com and follow the CRISPR tutorial from Fabio Ferreira on Digital DNA Design. [video]
- Extra Credit: Compare with other Genome Editing technologies like Restriction Enzymes, TALENs and ZFNs.
ref: Georg-san’s note
https://trembl.notion.site/Fabio-Ferreira-Digital-DNA-Design-ee1fcc3babfc469a85e510db8e89bdbd
CRISPR Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats CRISPR-AssociatedProteins 9) is a method that can knock out or knock in any gene easily, rapidly, and with high efficacy.
Crisper was developed based on the immune system of bacteria, and is a method of DNA double-strand breakage. It’s a breakthrough in gene editing because all you need is the enzyme Cas9 and sgRNA, which can be handled in a general laboratory.
It is possible to knock out a specific gene sequence or insert yet another sequence by creating a short sgRNA that contains a complementary sequence to the target DNA, and then a protein called Cas9 bound to the sgRNA attaches to the DNA and cleaves it.

*PAM (protospacer adjacent motif) is a short sequence of bases adjacent to the target DNA, and it activates the nuclease domain of Cas9.
The function of the repair of cleaved DNA can be divided into two categories: homology-directed repair (HDR)「相同組換え型修復」 and mon-homologous end joining (NHEJ)「非相同末端結合」. In HDR, the cell uses DNA with a sequence similar to the double strand breaks as a template and performs the repair exactly according to the template DNA sequence. Therefore, by providing the cell with a template DNA containing the DNA sequence to be modified, the modification can be introduced into the genomic DNA. In NHEJ, on the other hand, the cell joins the two ends of the double strand breaks with random DNA insertions and deletions.
test Benchling
I followed Fabio’s lecture briefly.